The UK is facing an economic crisis

Modern modifications in the UK’s major work have experienced a positive effect on pound sterling and very long-phrase sovereign bond yields. But the money industry response has been muted in contrast with the monetary turmoil blamed on former primary minister Liz Truss and ex-chancellor Kwasi Kwarteng in current months.
After the mini-finances on September 23, the marketplaces reacted to a undesirable policy: Truss’s tactic to undertake enormous tax cuts without the need of delivering a great deal certainty on how this would be funded. Its reversal brought bond yields down from the latest highs (primarily cutting down the value of governing administration borrowing) and observed the pound enjoy. But overall, the market losses seen next the mini-budget have scarcely been recovered.
To traders, audio and secure financial insurance policies make any difference much additional than the person residing in Selection 10. And that’s why, even with a new primary minister, current sector actions show buyers go on to see much more significant concerns with the Uk economy, the two quickly and about the extended time period.
In the limited time period, yields on Uk sovereign bonds have shot up after the mini-funds, raising the government’s price of borrowing. The deficiency of an accompanying forecast by the Business of Budgetary Responsibility (OBR) exacerbated this unfavorable reaction.
Prior to this, the Financial institution of England had been thinking about a bond-offering work out to attempt to deliver soaring inflation again to its 2% concentrate on by decreasing the offer of revenue in circulation (this is acknowledged as quantitative tightening). As a substitute, it had to immediately improve course just after the mini-funds. It not only postponed this tightening, but also restarted quantitative easing and bond buys, promising to invest in up to £10 billion in gilts for every day to tackle a relevant crisis amongst pension funds.
Two factors will now establish upcoming sovereign bond produce dynamics and dictate govt borrowing expenses.
Very first, clarity on how extensive the Bank of England designs to carry on its policy of quantitative easing (purchasing bonds to hold yields lower) just before it reverts to quantitative tightening yet again. Markets are observing these steps quite meticulously and any suggestion that this assistance by the Bank will be lower off could make traders and investors nervous.
Next, the government’s medium-expression fiscal program, at this time scheduled for Oct 31, will also impact bond yields. In contrast to the mini-finances, this plan will arrive with an in-depth assessment from the OBR, offering marketplaces much more information. As well as, the present chancellor, Jeremy Hunt, has brought some of the fiscal strategy actions ahead to simplicity marketplace considerations.
It’s even now unclear what type of prepare it will be, however. A credit card debt-cutting system from Hunt and the new governing administration headed by Rishi Sunak should really guarantee the marketplaces about the UK’s fiscal stability, but it is nonetheless not known whether this would transpire by using more taxes or much less investing. Some proof on what would be ideal for the economic climate supports boosting capital revenue taxes (cash gains tax and inheritance tax) somewhat than chopping public expending or boosting profits taxes.
In the long term, the UK’s big problems are stagnating expansion and deficiency of productivity. And if the new governing administration addresses current challenges by increasing taxes and cutting paying out – together with greater interest costs from the Bank of England – there will be far more economic suffering.
Altering worldwide financial system
Many international locations are struggling related difficulties to the British isles, contributing to a weak international financial outlook in general proper now. Right after a extended period of time of traditionally ultra-minimal curiosity prices, boosts – so-called normalisation of financial coverage – ended up anticipated in most countries. But a sharp surge in inflation owing to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and pandemic-period supply chain difficulties have prompted most central banks to scramble to tighten financial policy even additional by escalating prices additional quickly.
Current amount adjustments by central banks
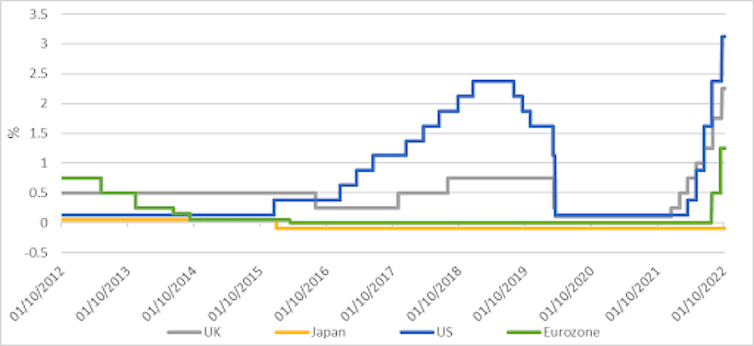
Author’s chart employing Financial institution for International Settlements facts.
These fee hikes and coverage tightening techniques by central banking companies could build major monetary and fiscal instability. Now, the US Federal Reserve’s unwinding of its equilibrium sheet from a peak of US$8.97 trillion (£7.9 trillion) in April 2022, for illustration, prompted the dollar to take pleasure in by far more than 13% in the final 6 months. This has designed challenges for emerging sector currencies, as well as big currencies – the yen, pound sterling and the euro – which have all depreciated substantially versus the US greenback.
This has additional to inflationary pressures, specially in the Eurozone and Uk, but it also affects sovereign bond yields, demanding economic steadiness in these nations. Given that August, the value of borrowing has additional than doubled for many.
The climbing value of government borrowing
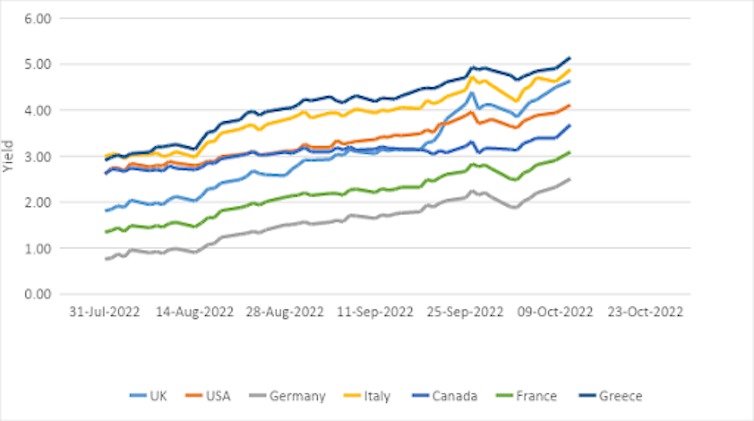
Author’s chart making use of Thomson Reuters details.
But to address soaring inflation, even additional central banking companies will want to shrink their harmony sheets by offering bonds. The whole sizing of the asset invest in programmes of the main four central banks alone is about US$26.7 trillion. With a weak international economic system and these other economic fragilities, this is likely to be a unpleasant exercising for the global financial system.
Without a doubt, these kinds of tightening will maximize the value of authorities borrowing further more, creating big challenges, particularly for really leveraged governments, and all those nonetheless paying out off pandemic-era help this kind of as the British isles and Eurozone.
The British isles specially, is also dealing with a change in the international economic centre of gravity absent from its overall economy. In considerably less than two a long time, the United kingdom has shrunk in relative phrases from being an financial system bigger than China to remaining about 9 times lesser. And the pound no extended enjoys the exact same standing as the US dollar, this means monetary markets will punish it severely if it ways out of line.
This indicates the new United kingdom government faces a tricky undertaking in reigniting world wide investor self esteem in its financial security, even with a new prime minister extensively viewed as a continuous hand.![]()
Muhammad Ali Nasir, Associate Professor in Economics, College of Leeds
This report is republished from The Discussion below a Imaginative Commons license. Go through the primary post.